Unit 5: Habitats
The Food Chain
A Simple Food Chain
A food chain shows how each living organism gets food and how food passes from one organism to another. In a food chain there are producers, consumers and decomposers.
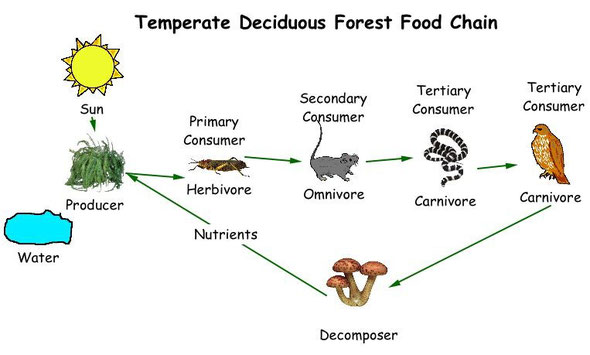
Producers
Green plants make their own food by using water and nutrients from the soil and energy from the Sun. Plants are producers.
Consumers
Most organisms can't produce their own food and so they must eat other organisms. These are called consumers.
Predators
A consumer that captures and eats another animal is called a predator. Prey is the animal eaten by the predator.
Decomposers
Worms, bacteria and fungi are decomposers. They eat dead plants and animals. Then they release nutirents back into the soil so plants can use them to produce their own food.
Online Activities
Food Chain Games
http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/content/animals/kidscorner/games/foodchaingame.htm
http://www.ecokids.ca/PUB/eco_info/topics/frogs/chain_reaction/play_chainreaction.cfm
http://www.coolclassroom.org/cool_windows/home.html
Land Habitats
Deserts
Deserts are very dry, because they get very little rainfall. They are very hot during the day and very cold at night. The organisms that live in a desert like cacti, scorpions and ants have
adapted to these difficult conditions.
Rainforests
Rainforests are wet places with heavy rainfall, lots of sunlight and warm air. Rainforests are home to many different types of plants and trees and thousands of animal species.
The Arctic Region
The Arctic region has very low temperatures and low rainfall. The animals in the arctic have adapted to very low temperatures.
Grasslands
Grasslands don't have much rainfall but they do have hot summers and cold winters. The soil is poor so there are not many trees. There is, however, a lot of grass.
Forests
Forests are places dominated by evergreen and deciduous trees. Deciduous trees lose their leaves in autumn and grow new ones in spring. Evergreen never lose their leaves.
Online Activities
Build an animal habitat.
http://switchzoo.com/games/habitatgame.htm
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/scienceclips/ages/10_11/interdependence_fs.shtml
Water Habitats

Oceans and seas are saltwater habitats.

A pond is a small area of fresh water. It doesn't have moving water

Rivers are streams of moving water. Animals that live in rivers are adapted to fast flowing water. River banks are also home to many animals.
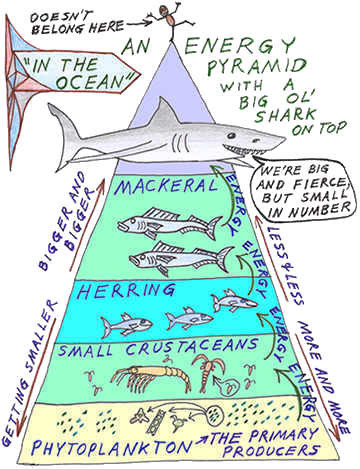
An Ocean Food Chain
1. Phytoplankton are producers. They are microorganisms that create energy using photosynthesis.
2. Small floating animals like shrimps or jellyfish called zooplankton, eat phytoplankton. Zooplankton are consumers.
3. Small fish, like sardines, eat zooplankton.
4. larger fish like Mackerel, eat sardines. Mackerel is a consumer too.
5. Sharks eat mackerel. The shark is a predator, the mackerel is its prey.
Adaptations
Organisms adapt to their environments. Their adaptations can be physical or behavioural.
Physical Adaptations
This is the evolution of an organism's body that helps the organism to find food, defend itself and reproduce.

Stick insects protect themselves by imitating the colours and shape of plants.

Chameleons change colour to match their surroundings.

Porcupines developed spines to protect themselves.

Skunks have special glands that spray a toxic substance at predators.
Behavioural Adaptations
A behavioural adaptation is a change in an animal's behaviour that helps it to interact with its habitat.

Animals migrate from one place to another.

Bears hibernate in winter.

Desert animals are active at night to avoid the heat of the day.
Populations and Communities
Populations
Populations are groups of organisms of the same species which live together in the same geographical area. Populations grow when there is enough food, water and shelter.
Communities
A community is a group of different species that live together and interact in the same geographical area. In a community there are both predators and prey. Living things in a community depend on each other to live.
 2º 3º 4º
2º 3º 4º




